Detectors¶
Detectors are used to collect the weights of photon packets that escape the
sample or to collect the weight of photon packets that are specularly
reflected when launching with the selected source.
The the two detector locations can be populated and passed to the Monte Carlo
simulator through the xopto.mccyl.mcdetector.base.Detectors.
All the detector types that can be used in the Monte Carlo simulator
are implemented by subclassing xopto.mccyl.mcdetector.base.Detector.
The xopto.mccyl.mcdetector module includes two different detectors:
xopto.mccyl.mcdetector.total.Totalimplements a detector that collects the weight of photon packets into a single accumulator.xopto.mccyl.mcsdetector.fiz.FiZimplements a 2D detector that collects the photon packets according to their polar angle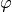 and
and  location when leaving the sample and entering
the surrounding medium`.
location when leaving the sample and entering
the surrounding medium`.
The individual detectors are conveniently imported into the
xopto.mccyl.mc and xopto.mccyl.mcdetector modules.
FiZ¶
The following example shows how to create a
FiZ detector
that collects photon packets with polar angle 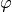 from -180° to
180° (1° step) and
from -180° to
180° (1° step) and  coordinate from -1 to 1 mm
(10 μm step). Distribution of accumulators along the two axis
is defined by
coordinate from -1 to 1 mm
(10 μm step). Distribution of accumulators along the two axis
is defined by Axis.
from xopto.mccyl import mc
import numpy as np
det = mc.mcdetector.FiZ(
fi=mc.mcdetector.Axis(np.pi, np.pi, 360),
z=mc.mcdetector.Axis(-1.0e-3, 1.0e-3, 200)
)
Note
The valid range of polar angle 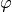 is from
is from 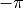 (-180°) to
(-180°) to 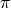 (180°). The first and last accumulator along the
polar
(180°). The first and last accumulator along the
polar 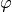 and
and  axis also collect the weight of all the
photon packets that exceed the lower and upper bounds of the range.
axis also collect the weight of all the
photon packets that exceed the lower and upper bounds of the range.
Total¶
To collect the weights of photon packets that leave the sample into a single
accumulator, use the xopto.mccyl.mcdetector.total.Total detector.
Note that parameters cosmin and direction can be optionally
used to limit the acceptance cone of the detector.
from xopto.mccyl import mc
det = mc.mcdetector.Total()
Use in Monte Carlo simulator¶
To use the detectors in Monte Carlo simulations, we need to populate an instance
of xopto.mccyl.mcdetector.base.Detectors, that can independently set
the detectors at the outer sample surface and the detector for
photon packets that are specularly reflected at the medium-sample boundary
when launched. Note that it is not required to populate the two detectors
(outer and specular) as illustrated in this example.
from xopto.mccyl import mc
outer = mc.mcdetector.FiZ(
fi=mc.mcdetector.Axis(-np.pi, np.pi, 360),
z=mc.mcdetector.Axis(-1.0e-3, 1.0e-3, 200)
)
specular = mc.mcdetector.Total()
detectors = mc.mcdetector.Detectors(outer=outer, specular=specular)
After completing the Monte Carlo simulations, the returned instance of
Detectors can be used to access the
collected reflectance (also used for transmittance) or the accumulated raw
weight of the photon packets.
Note
The reflectance / transmittance is computed as the raw weight in the accumulator divided by the number of launched photon packets and if applicable also divided by the surface area of the accumulator (weight/m 2).
outer_reflectance = detectors.outer.reflectance
outer weight = detectors.outer.raw
specular_reflectance = detectors.specular.reflectance
specular_raw weight = detectors.specular.raw